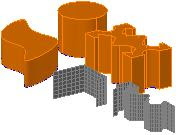
Create models of free form shapes


Models that change from one shape to another
Change the size and orientation in 3D space

- Geometry consists of two closed loop cross sections, one a circle and the other a polyline; and three open loop cross sections, two lines and a spline
- Surface model created by selecting the open loop geometry as the cross sections and the closed loop geometry as guides
- Solid model created by selecting the closed loop geometry as the cross sections and the open loop geometry as guides
- Solid model created by selecting the closed loop geometry as the cross sections and the spline on the right as a path
- Solid model created by only selecting the closed loop geometry and selecting the Ruled loft setting
- Solid model created by only selecting the closed loop geometry and selecting the Smooth Fit loft setting
- Solid model created by only selecting the closed loop geometry and selecting the Draft Angles loft setting with a 90 degree start angle and end angle for 50% of the distance