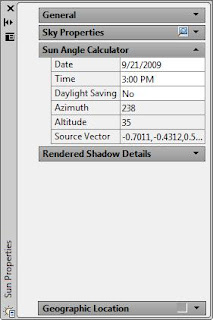
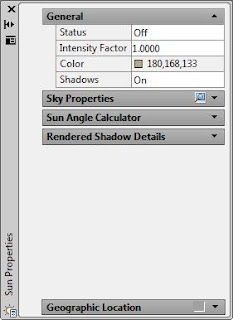
After render a scene, the output is either displayed directly in the current viewport or in the Render window
If want to generate a file from a rendering, the rendering must be done in the Render window and not the viewport

Image pane: displays the current render in progress
Statistics pane: displays the information about the selected image in the History pane
History pane: displays the most recent renderings of the current drawing that have been done in the Render window